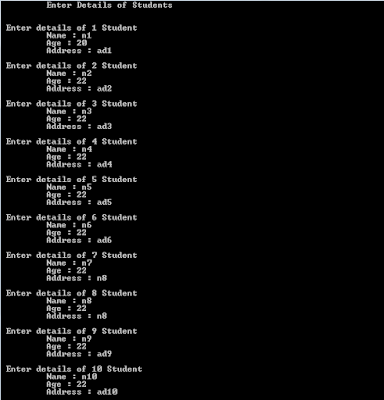
Create a class 'Student' with three data members which are name, age and address. The constructor of the class assigns default values name as "unknown", age as '0' and address as "not available". It has two members with the same name 'setInfo'. First method has two parameters for name and age and assigns the same whereas the second method takes has three parameters which are assigned to name, age and address respectively. Print the name, age and address of 10 students.
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class student{
int age;
string name, add;
public:
student()
{
name="unknown";
age=0;
add="not available";
}
setinfo(char nam[20], int ag)
{
name=nam;
age=ag;
cout<<"Details of student is"<<endl;
cout<<"Name : "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"Age : "<<age<<endl;
}
setinfo(string nam, int ag, string addres)
{
name = nam;
age= ag;
add=addres;
}
void display()
{
cout<<"Name : "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"Age : "<<age<<endl;
cout<<"Address : "<<add<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
int j=10;
student s[j];
int age;
string name, add;
cout<<"\t Enter Details of Students"<<endl;
cout<<"\n"<<endl;
for (int i=0; i<j; i++)
{
cout<<" Enter details of "<<i+1<<" Student"<<endl;
cout<<"\t Name : ";
cin>>name;
cout<<"\t Age : ";
cin >>age;
cout<<"\t Address : ";
cin>>add;
s[i].setinfo(name, age, add);
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<"\t Displaying Details of Students Entered"<<endl;
cout<<"\n"<<endl;
for(int i=0; i<j; i++)
{
cout<<"\n Details of "<<i+1<<" Student is"<<endl;
s[i].display();
}
}